Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming the landscape of healthcare, particularly in cardiology, where non-invasive hemodynamic monitoring (NIVM) is becoming increasingly important. This systemic review focuses on the accuracy, effectiveness, and clinical applicability of AI technologies in NIVM, shedding light on their potential to enhance patient outcomes and improve clinical practices.
Understanding Hemodynamic Monitoring
Hemodynamic monitoring is critical in assessing vascular and cardiac function, guiding interventions in critically ill patients, and improving overall morbidity and mortality rates. Traditionally, hemodynamic parameters such as cardiac output, stroke volume, and systemic vascular resistance were measured using invasive techniques, which can pose risks to the patient.
Non-invasive methods, which include echocardiography, photoplethysmography, and bioimpedance, offer a safer alternative. However, these methods often require skilled personnel for interpretation, making AI a promising avenue for improvement.
The Emergence of AI in NIVM
AI technology leverages algorithms and machine learning to analyze complex datasets more efficiently and accurately than traditional methods. AI can interpret large volumes of data gathered through non-invasive techniques, prioritize information, and provide actionable insights in real time.
For instance, studies using AI-driven algorithms have demonstrated improved accuracy in estimating cardiac output compared to traditional Doppler echocardiography. The use of AI allows for quicker decisions that can significantly enhance patient care, especially in emergency settings.
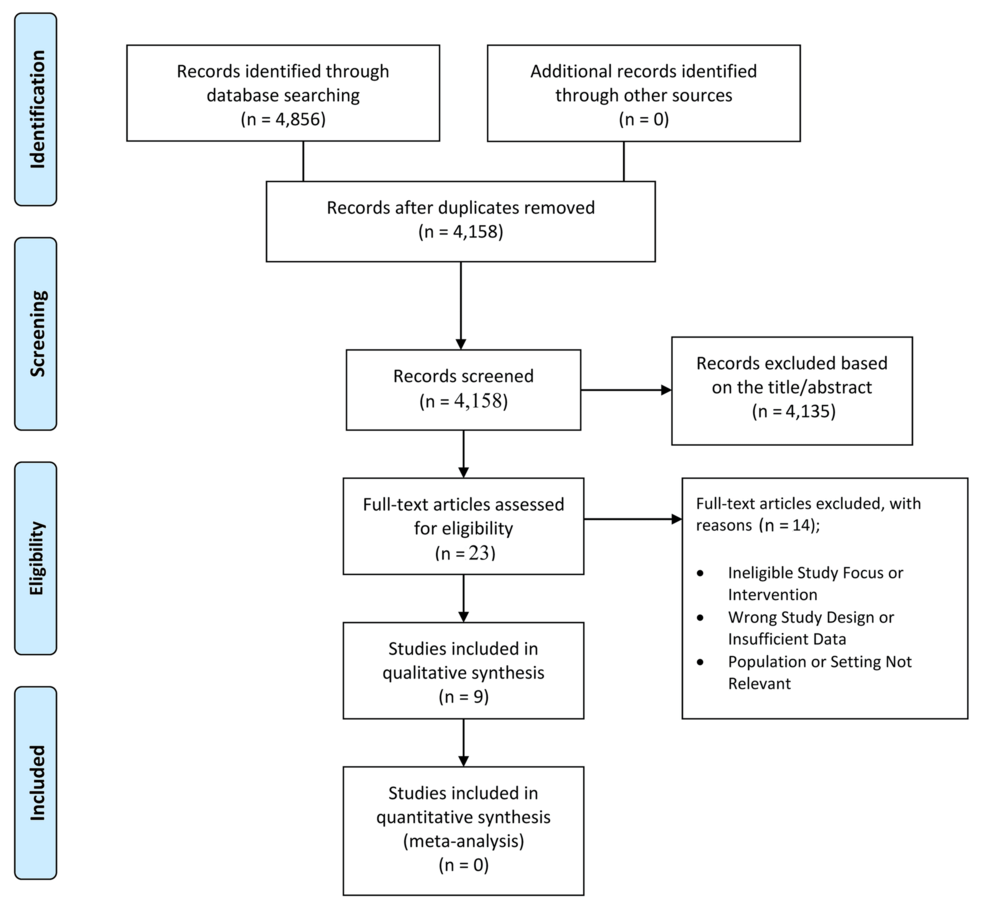
Systematic Review of Recent Findings
A systematic review of literature from the last three years reveals several key insights regarding the accuracy and effectiveness of AI in non-invasive hemodynamic monitoring:
Enhanced Accuracy:
AI algorithms, notably those based on deep learning, have been shown to outperform traditional methods in estimating hemodynamic parameters. Studies demonstrated that AI systems can achieve higher correlation coefficients with invasively measured values.Clinical Applicability:
AI tools have successfully been integrated across various clinical settings, from the operating room to intensive care units. Their ability to provide continuous monitoring without the drawbacks of invasive techniques makes them appealing in high-stakes environments.User-Friendliness:
Interfaces designed using AI are often user-centric, making it easier for healthcare providers to adopt these technologies quickly. This is crucial, as quick decision-making is a cornerstone of effective patient management in cardiology.- Predictive Capabilities:
Some AI models can predict hemodynamic instability before it occurs, providing lead time for interventions. This predictive power is a promising dimension in managing critically ill patients where every second counts.
Challenges and Issues
While the potential for AI in NIVM is significant, several challenges must be addressed:
Data Quality and Quantity:
AI systems rely on large datasets to learn and improve. In cardiology, data may be scarce or inconsistent, impacting the training of AI models. Standardization of data collection is needed to enhance model performance.Interpretability:
One of the major barriers to adopting AI technologies in healthcare is the "black-box" nature of many algorithms. Clinicians often demand transparency and an understanding of how AI arrives at its conclusions to trust its recommendations.Regulatory Hurdles:
The integration of AI technologies into clinical workflows must navigate complex regulatory frameworks. Ensuring that these tools comply with healthcare regulations while also demonstrating safety and efficacy is crucial.- Ethical Considerations:
AI raises ethical concerns, particularly related to data privacy and the potential for biases in decision-making. Ensuring that AI systems are trained on diverse datasets can help mitigate these biases.
Future Directions
The future of AI in non-invasive hemodynamic monitoring appears promising. Emerging technologies, including advanced machine learning techniques and wearable sensors, present opportunities for further advancements.
Continuous Learning:
Future AI systems may incorporate continuous learning, adapting to new patient populations and improving their accuracy and precision over time.Integration with Other Technologies:
The fusion of AI with telemedicine and remote monitoring tools could be revolutionary, providing real-time hemodynamic data to care teams regardless of their geographical location.- Multi-disciplinary Collaboration:
Collaboration among clinicians, data scientists, and engineers will be crucial for advancing AI applications in hemodynamic monitoring. Such interdisciplinary efforts can lead to the development of comprehensive solutions tailored to clinical needs.
Conclusion
AI’s incorporation into non-invasive hemodynamic monitoring represents a transformative shift in cardiovascular care. Its ability to enhance accuracy, effectiveness, and clinical applicability can lead to improved patient outcomes, although challenges in data quality, interpretability, and regulatory compliance must be addressed. The future is bright as ongoing research and technological advancements promise to make AI an integral part of cardiology practice. Through a systematic approach and collaborative efforts, AI has the potential to significantly redefine hemodynamic monitoring, making it safer and more effective for clinicians and patients alike.
In the rapidly evolving field of self-care and patient monitoring, embracing AI-driven tools can unlock unprecedented capabilities, setting the stage for a new era in personalized and proactive cardiological care.